
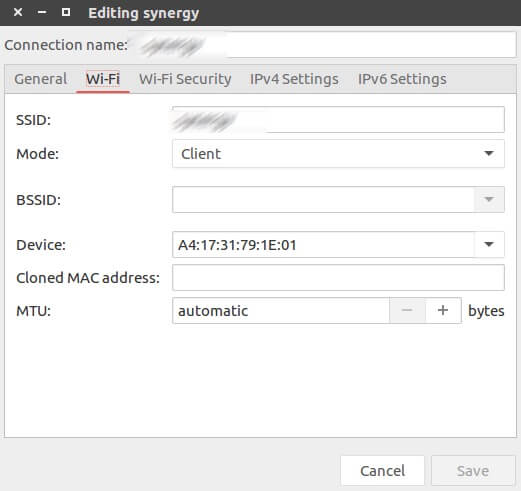
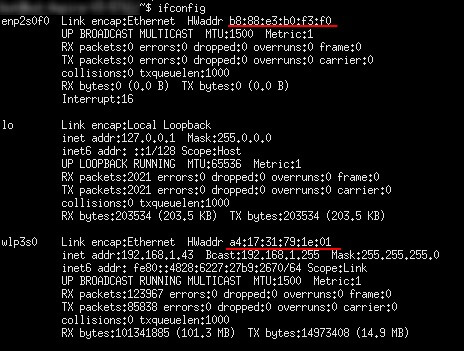
The local computer only knows its source/destination IP and its source MAC addresses. The destination hardware address is unknown, so the ICMP echo request is put on hold.Unfortunately, the local computer does not know the MAC address… it only knows the IP address. The local computer sends a ping (ICMP echo request) to a destination IP address (remote computer) within the same segment.The following message flow diagram can help you understand the concept: Understanding how ARP works can help you find IPs and MAC addresses quickly. Their frames encapsulate packets that contain IP address information.Ī device must know the destination MAC address to communicate locally through media types like Ethernet or Wifi, in layer 2 of the OSI model. As you might already know, devices in the data link layer depend on MAC addresses for their communication. It operates with frames on the data link layer.
#My mac address lookup how to#
Related post: How to Scan network for IP Addresses Understanding ARPĪRP (Address Resolution Protocol) is the protocol in charge of finding MAC addresses with IPs in local network segments. In this article, we’ll show you how to find all ip addresses on a network along with device vendors using MAC addresses with different methods for free. But RARP is an obsolete protocol with many disadvantages, so it was quickly replaced by other protocols like BOOTP and DHCP, which deal directly with IP addresses. Or your computer is unable to display its IP due to various reasons, and you are getting a “No Valid IP Address” error.įinding the IP from a known MAC address should be the task of a ReverseARP application, the counterpart of ARP. You might be in a situation where you don’t have the IP address of a device in a local network, but all you have is records of the MAC or hardware address.
This can be contrasted to a programmed address, where the host device issues commands to the NIC to use an arbitrary address.How would you communicate with a device when you don’t have the IP? It may also be known as an Ethernet hardware address (EHA), hardware address or physical address (not to be confused with a memory physical address). If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer's registered identification number and may be referred to as the burned-in address (BIA). MAC addresses are most often assigned by the manufacturer of a network interface controller (NIC) and are stored in its hardware, such as the card's read-only memory or some other firmware mechanism. Logically, MAC addresses are used in the media access control protocol sublayer of the OSI reference model. MAC addresses are used as a network address for most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
#My mac address lookup full#
If you want to find the manufacturer a certain MAC address belongs to, enter your full MAC address or first 6 hexadecimal digits. How to use this tool to find the manufacturer and other details from MAC address?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
